IQ scores are distributed along a bell curve, with the majority of the population scoring near the average range. Approximately 68% of individuals globally fall within the average IQ range of 85 to 115. With a standard deviation of 15, the average IQ score is represented by the median point of 100.
A significant portion of the population has a cognitive ability that is considered average. Only 98% of people have an IQ score below 130. Just 2% of the population scores above average.
IQ scores are typically distributed along a bell curve, which is also referred to as a normal distribution. In this distribution, most people score around the average IQ, which is set at 100. This score, 100, serves as the midpoint of the IQ scale. Scores above 100 suggest above-average intelligence, while scores below 100 suggest below-average intelligence. The majority of the global population falls within the range of 85 to 115, covering approximately 68% of individuals. The bell curve illustrates that fewer people score extremely low or extremely high IQ scores, with the majority falling within one standard deviation (15 points) of the average.
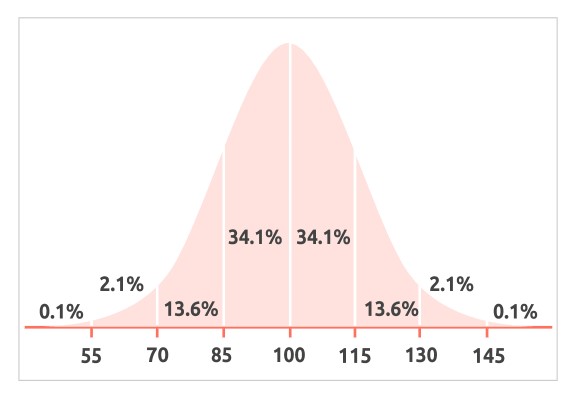
Here's a rough breakdown of IQ scores and their distribution:
Almost all IQ tests are built to assess two primary facets of cognitive ability: crystallized intelligence and fluid intelligence. Crystallized intelligence is the knowledge and skills acquired over a lifetime, reflecting one's accumulated learning and experiences. In contrast, fluid intelligence includes the capacity for reasoning, problem-solving, and comprehending abstract information, independent of acquired knowledge.
While crystallized intelligence tends to increase with age, reflecting continued learning and experience, fluid intelligence is believed to peak in early adulthood and gradually decline thereafter. IQ tests, which are typically administered by licensed psychologists, aim to assess these different types of intelligence.
These tests often consist of various subtests, which evaluate different aspects of cognitive function such as mathematical abilities, language skills, memory, reasoning skills, and processing speed. Scores from these subtests are then combined to calculate an overall IQ score.
Several widely recognized IQ tests include:
These tests provide valuable insights into an individual's cognitive strengths and weaknesses, helping professionals make informed decisions regarding education, employment, and other areas of life.
This report aims to explore the average IQ statistics across different factors. By analyzing the statistics, we can gain insights into the global distribution of intelligence and understand how factors such as age, gender, and socioeconomic status may influence IQ scores. Understanding these trends can help us better understand human cognitive abilities and inform educational and social policies.
What is the average IQ globally? The global average IQ is estimated to fall within the range of 90 to 100. This range is derived from various studies and assessments conducted across different countries and regions worldwide. IQ scores are standardized to have a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15 in the general population. IQ scores can vary significantly among different populations due to factors such as socioeconomic status, education level, cultural background, and access to resources. Additionally, the methods used to measure IQ can also impact the results.
Some regions and countries may have average IQ scores that are higher or lower than the global average. Factors such as educational policies, healthcare systems, and economic conditions can influence the cognitive development and overall intelligence of a population.
The average IQ by country varies, and different studies may produce slightly different results. Here are the approximate average IQ scores for the top 10 countries with the highest IQ scores:
Top | Country | Average IQ score |
1 | Japan | 106.48 |
2 | Taiwan | 106.47 |
3 | Singapore | 105.89 |
4 | Hong Kong | 105.37 |
5 | China | 104.1 |
6 | South Korea | 102.35 |
7 | Belarus | 101.6 |
8 | Finland | 101.2 |
9 | Liechtenstein | 101.07 |
10 | Germany | 100.74 |
See also: Who has the highest IQ in the world?
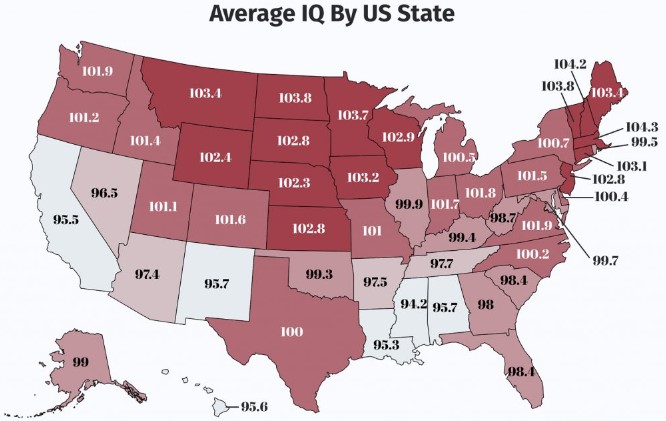
In the 2019 report "The Intelligence of the Nations," the average IQ in the U.S. was determined to be 97.43. This calculation incorporated various IQ tests and detailed sample data on social, economic, and environmental factors. State IQ scores, derived from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NEAP), were published in 2022. Here is a table of the average IQ in the U.S. by state:
No. | State | Average IQ | Rank |
1 | Alabama | 96.4 | 46 |
2 | Alaska | 99.4 | 22 |
3 | Arizona | 98.3 | 34 |
4 | Arkansas | 97.1 | 41 |
5 | California | 97.1 | 42 |
6 | Colorado | 101.1 | 11 |
7 | Connecticut | 101.2 | 9 |
8 | Delaware | 98.7 | 26 |
9 | Florida | 98.8 | 24 |
10 | Georgia | 98.1 | 36 |
11 | Hawaii | 99.2 | 29 |
12 | Idaho | 100.5 | 15 |
13 | Illinois | 99.4 | 21 |
14 | Indiana | 100.6 | 13 |
15 | Iowa | 101.1 | 12 |
16 | Kansas | 100.5 | 16 |
17 | Kentucky | 98.8 | 25 |
18 | Louisiana | 95.2 | 50 |
19 | Maine | 100.9 | 8 |
20 | Maryland | 100.0 | 18 |
21 | Massachusetts | 103.1 | 1 |
22 | Michigan | 99.6 | 20 |
23 | Minnesota | 102.9 | 3 |
24 | Mississippi | 95.8 | 49 |
25 | Missouri | 99.5 | 19 |
26 | Montana | 101.1 | 14 |
27 | Nebraska | 101.2 | 10 |
28 | Nevada | 96.6 | 45 |
29 | New Hampshire | 103.2 | 2 |
30 | New Jersey | 101.0 | 17 |
31 | New Mexico | 95.0 | 51 |
32 | New York | 98.4 | 31 |
33 | North Carolina | 99.5 | 23 |
34 | North Dakota | 101.7 | 5 |
35 | Ohio | 100.0 | 19 |
36 | Oklahoma | 98.2 | 37 |
37 | Oregon | 100.3 | 17 |
38 | Pennsylvania | 100.2 | 18 |
39 | Rhode Island | 99.4 | 28 |
40 | South Carolina | 97.8 | 33 |
41 | South Dakota | 100.7 | 7 |
42 | Tennessee | 98.3 | 35 |
43 | Texas | 97.4 | 40 |
44 | Utah | 101.5 | 6 |
45 | Vermont | 102.2 | 4 |
46 | Virginia | 101.2 | 10 |
47 | Washington | 101.5 | 6 |
48 | West Virginia | 97.2 | 43 |
49 | Wisconsin | 101.2 | 10 |
50 | Wyoming | 101.7 | 5 |
IQ scores can change over a person's lifetime. In childhood and adolescence, IQ scores can fluctuate as individuals develop and learn. Factors such as education, experiences, and opportunities can all impact IQ scores. However, research suggests that IQ scores tend to stabilize by adulthood, meaning that significant changes in IQ are less likely in adulthood compared to earlier stages of life. Here is a table showing age groups and their average IQ scores:
Age Group | Average IQ Score | Interpretation |
16-17 | 108 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
18-19 | 105 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
20-24 | 99 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
25-34 | 97 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
35-44 | 101 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
45-54 | 106 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
55-64 | 109 | Normal/Average Intelligence |
65-69 | 114 | Superior/Above-Average Intelligence |
70-74 | 119 | Superior/Above-Average Intelligence |
These scores are based on research and provide a general indication of average IQ scores for different age groups.
Examining average IQ statistics by profession offers an insight into how intelligence is distributed across various fields and industries. This exploration prompts two interesting questions : Are some professions more intellectually challenging than others? Do certain industries tend to attract individuals with higher IQ?
Here is the table of typical careers and the average IQ score:
Occupation | Average IQ score range |
Professional and Technical Jobs | 112 |
Managers | 104 |
Clerical and Sales Workers | 101 |
Skilled Trades | 101 |
Semi-skilled Trades | 92 |
Unskilled Occupations | 87 |
Surgeons and Physicians | 125-130 |
College Professors | 115-130 |
Electrical Engineers | 110-130 |
Lawyers | 115-130 |
School Teachers | 110-120 |
Chemists | 120-130 |
Social Workers | 90-110 |
Secretaries | 90-110 |
Firefighters | 90-110 |
Agriculture & Horticulture Workers | 90-110 |
Police Officers | 90-110 |
Professional Athletes | 90-110 |
Individuals in Artistic Professions | 90-110 |
Catering Trade | 90-110 |
Several factors can influence IQ scores, including genetics, environment, education, and upbringing. While genetics play a significant role in determining IQ, environmental factors such as access to education, nutrition, and socio-economic status also have a huge impact on an individual's IQ.
Genetics: Genetics plays an important role in determining someone’s IQ. Studies have shown that IQ scores tend to be more similar among biological relatives, suggesting a genetic component to intelligence. However, it's important to note that genetics is not the sole determinant of IQ and that environmental factors also play a crucial role.
Environment: Environmental factors such as access to education, nutrition, and socio-economic status can significantly impact IQ. Children who grow up in environments with limited access to quality education, nutritious food, and supportive resources may have lower IQ scores compared to children who grow up in more enriching environments.
Education: Education plays a crucial role in developing cognitive abilities and can have a lasting impact on IQ. Access to quality education can enhance cognitive skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and language abilities, all of which are reflected in IQ scores.
Upbringing: The way children are raised and the stimulation they receive in their early years can also influence IQ. Children who are raised in stimulating environments with opportunities for learning and exploration tend to have higher IQ scores compared to children who grow up in less stimulating environments.
Nutrition: Nutrition plays a critical role in brain development, and malnutrition during early childhood can have a lasting impact on cognitive abilities and IQ. Adequate nutrition, especially in the early years, is essential for optimal brain development and cognitive function.
Socio-economic Status: Socio-economic status can also impact IQ scores. Children from higher socio-economic backgrounds often have access to more resources, such as better schools, books, and educational opportunities, which can contribute to higher IQ scores compared to children from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Each Racial Group and IQ Scores
Historical studies have indicated variations in average IQ scores among different racial groups, leading to ongoing debate and controversy. "The Bell Curve" ignited discussions by suggesting genetic disparities in IQ, implying that some racial groups might be inherently more or less intelligent. However, critics contend that environmental factors, such as access to education and socioeconomic status, play a more significant role in these differences. The American Psychological Association conducted research but found no direct evidence supporting genetic explanations for the observed racial IQ score variations, reinforcing the complex and multifaceted nature of intelligence and its assessment.
Nationality Differences in Average IQ Scores
Research indicates that there are differences in average IQ scores among various nations, with environmental factors such as education and socioeconomic status playing a significant role. For example, Hong Kong has been reported to have the highest average IQ score, around 108, while Equatorial Guinea has one of the lowest, at approximately 59. These variations highlight the impact of environmental influences on cognitive abilities and the importance of considering such factors when interpreting IQ scores on a national scale.
Sex Differences in Average IQ Scores
Some studies suggest no average IQ difference between men and women, but there may be more variability in scores among men. However, there is evidence to suggest that there may be more variability in IQ scores among men, with a slightly higher proportion of men scoring at both the high and low ends of the IQ spectrum. These differences in performance on various tasks, such as verbal and spatial tasks, are thought to be influenced by a combination of biological and environmental factors, including genetics, hormones, brain structure, culture, and education. Overall, the issue of sex differences in IQ remains complex and requires careful consideration of multiple factors.
What does it mean to have an average IQ?
Having an average IQ typically means scoring around 100 on an IQ test. This score is considered to be the average intelligence level for the general population. It means that your reasoning and problem-solving skills are at an average level. People with an average IQ are considered to have normal cognitive abilities compared to the rest of the population.
What is considered a high IQ?
A high IQ is generally considered to be a score above 130. This score is considered to be above average and indicates a high level of cognitive ability. People with high IQs often excel in tasks that require logical reasoning, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
See also: What is a good IQ score?
Who has the lowest IQ in the world?
It's important to note that IQ scores are not a definitive measure of intelligence, and various factors can affect an individual's score. Additionally, it is not appropriate or respectful to label or identify individuals based on their IQ scores.
Understanding what is average IQ provides valuable insights into the distribution of cognitive abilities in the population. While IQ is influenced by genetics and environment, it is not a definitive measure of intelligence. Instead, it serves as a tool for assessing cognitive abilities and understanding the factors that contribute to intellectual development.