Are you ready to challenge your cognitive ability? An IQ test can give you a lot of information about your actual intelligence or the way you solve problems. But what kind of questions are on an IQ test? This article will reveal the most common types of questions that are most often included in IQ tests, which will let you know what to expect.
IQ tests are not simply items that require selecting the right answer from several answer choices; they involve multiple areas and aspects of intelligence, such as problem-solving skills. These tests include varying questions so as to assess distinct mental abilities possessed by the client. By familiarizing yourself with the diverse question types in IQ tests, you can not only improve your test performance but also gain a deeper appreciation of your cognitive abilities. This understanding can lead to better educational and career choices tailored to your intellectual strengths and preferences.
Verbal reasoning questions measure your performance in comprehending texts which you comprehend as well as read. Specifically, they evaluate how well you can read and understand text and analyze information. There are two main types of questions in the verbal reasoning category.
1.1. Word Analogies
Word analogies involve finding the relationship between a pair of words and then identifying another pair of words with a similar relationship. These questions are frequently used in standardized tests (such as the SAT or GRE), cognitive capacity assessments, and linguistic ability tests.
Examples:
Example 1: Cat is to Kitten as Dog is to ?
Answer: Puppy
Example 2: Bird is to Fly as Fish is to ?
Answer: Swim
Skill required:
1.2. Sentence completion
Sentence completion questions require the test taker to select the best word or words to complete a given sentence logically and grammatically.
Examples:
Example 1: Although he was tired, he ? to finish his homework.
Answer: managed
Example 2: The professor’s lecture was so ? that all the students understood the complex topic.
Answer: clear
Skills required:
Numerical reasoning entails understanding of numbers as well as mathematical reasoning with a lot of ease. To answer the number reasoning questions, you need to have the ability to comprehend, evaluate, and analyze basic numerical tables and trends, as well as any corresponding patterns. In the numerical reasoning category, there are two sub-category types: arithmetic problems and number pattern.
2.1. Arithmetic problems
Arithmetic problems involve basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Examples:

Skills required:
2.2. Number pattern
Number series questions require identifying the pattern or rule that governs a sequence of numbers and predicting the next number in the series.-
Examples:
Example 1: Which number follows this series: 2, 4, 6, 8, …?
Answer: 10
Example 2: Which number follows this series: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5,... ?
Answer: 8
Skills required:
Spatial Reasoning questions evaluate a candidate’s aptitude to interpret spatial objects or figures two-dimensional or 3D. All the connections with links or space identity, the ability of understanding or reasoning about the items featured, as well as the memory-related skills for recalling such connections, are all gauged in the test. In the IQ test, there are three main types of spatial reasoning question:
3.1. Visual puzzles
Visual puzzles involve identifying patterns, shapes, or completing images based on visual cues.
Examples:

Example 1: Identifying the missing piece in a puzzle
Skills required:
3.2. Pattern recognition
Pattern recognition questions require identifying the recurring theme or rule in a set of figures or designs.
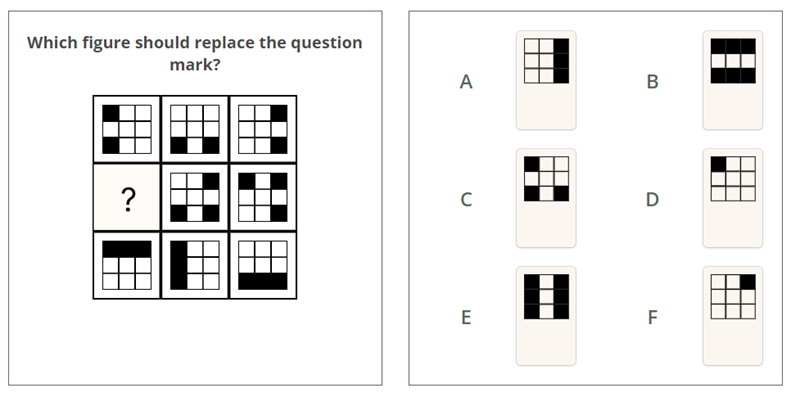
Skills required:
3.3. Three-dimensional (3D) rotation
3D rotation questions involve visualizing how a three-dimensional object would look if rotated.
Example:
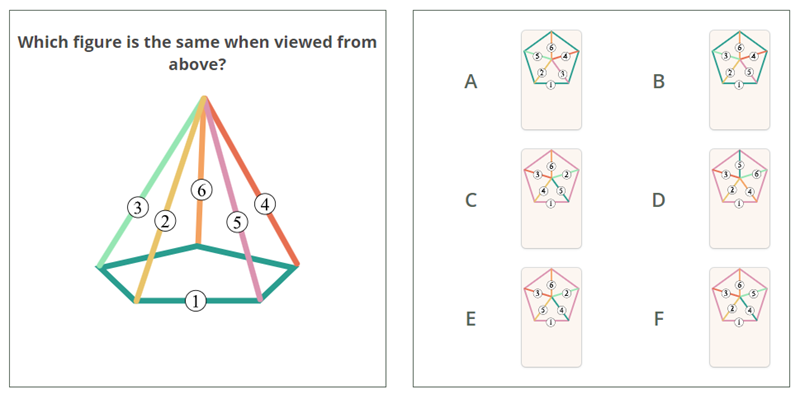
Skills required:
Questions belonging to the logical reasoning field can be solved with the help of logical ability of the candidates. It actually incorporates most of the question form concepts and then there are some implicit concept based creative ones.
4.1. Deductive reasoning
These questions involve drawing logical conclusions from given premises or statements.
Examples:
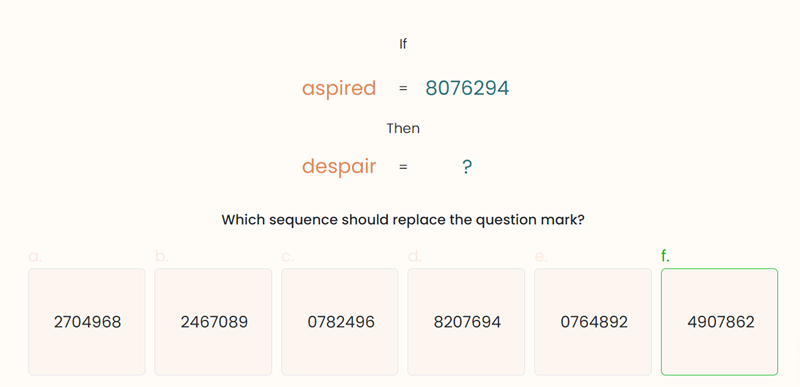
Skills required:
4.2. Logical sequences
Logical sequences involve determining the order or arrangement of items based on a set of rules or patterns.
Skills required:
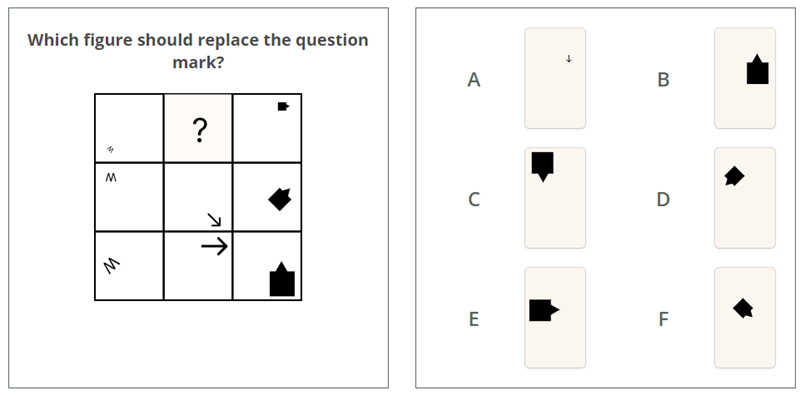
The types of questions that appear in an IQ test and they determine whether you are able to memorize and recall information. These questions typically involve:
5.1. Short-term memory
Short-term memory tasks involve recalling information presented briefly and immediately.
Example: Remember a list of words presented for a few seconds, then recall a series of numbers or letters.
Skills required:
5.2. Long-term memory
Long-term memory tasks involve recalling information stored over a longer period.
Example: Recall historical facts or events.
Skills required:
Read more: How is IQ measured?
IQ tests are designed to assess a variety of cognitive skills, each contributing uniquely to the overall IQ score. The primary types of questions found in IQ tests evaluate verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
Verbal reasoning questions assess the ability to understand, use, and think with spoken language. They measure skills such as vocabulary, the ability to see relationships between concepts (similarities), and comprehension. These skills are crucial for tasks requiring detailed understanding and effective communication. In the context of IQ scoring, verbal comprehension is significant, especially in verbal IQ tests, where it often comprises a substantial portion of the overall score.
Numerical reasoning questions test how a candidate calculates and their capacity of executing. These tasks include numerical concepts, computation, arithmetic word problems, and analysis of graphs and tables. Numerical reasoning is essential for technical disciplines that involve significant use of numbers, for example, financial engineering, civil engineering, physical, or natural sciences. From the problems faced in learning mathematics, it enables solution finding and logical reasoning, thus promoting success in learning as well as at the workplace.
Spatial reasoning questions evaluate non-verbal and spatial reasoning skills. These include block design tasks that involve analyzing and synthesizing abstract visual stimuli, as well as matrix reasoning and visual puzzles. Perceptual reasoning is critical for solving problems without relying on verbal information, helping individuals understand and manipulate visual data. In non-verbal IQ assessments, perceptual reasoning contributes significantly to the overall cognitive ability score.
Logical reasoning questions assess the ability to quickly and accurately process simple or routine visual information. These include tasks such as symbol search, coding, and cancellation. Speed of processing refers to the speed at which information is processed in the cognitive system where speeds are relatively adjusted to measure performance on different tasks.
Memory and recall questions measure the capacity to store and manipulate information over short periods. This includes tasks like digit span, which assesses attention, concentration, and mental control, and arithmetic problems. Working memory is fundamental for tasks that require the temporary storage and manipulation of information, influencing learning and comprehension. It is integral to both verbal and non-verbal IQ components, underpinning the ability to follow instructions and solve problems in real-time.
In conclusion, an IQ test might comprise several types of questions: verbal reasoning, numerical reasoning, spatial reasoning, logical reasoning, logical reasoning, and memory and recall. Understanding these cognitive skills and their contributions to overall IQ scores helps in appreciating how different question types in IQ tests are designed to measure diverse aspects of intelligence, reflecting their real-world applicability and relevance.